Clinical orthopedic examination (lameness examination)
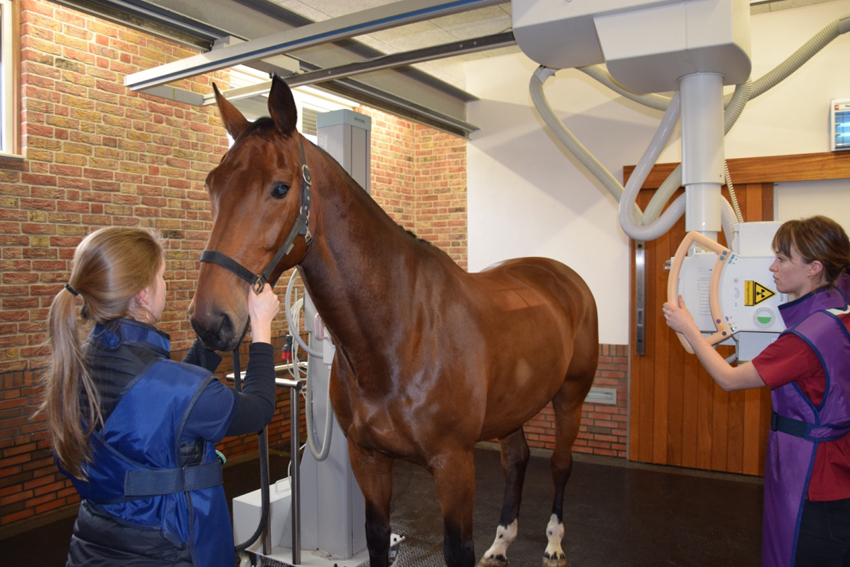
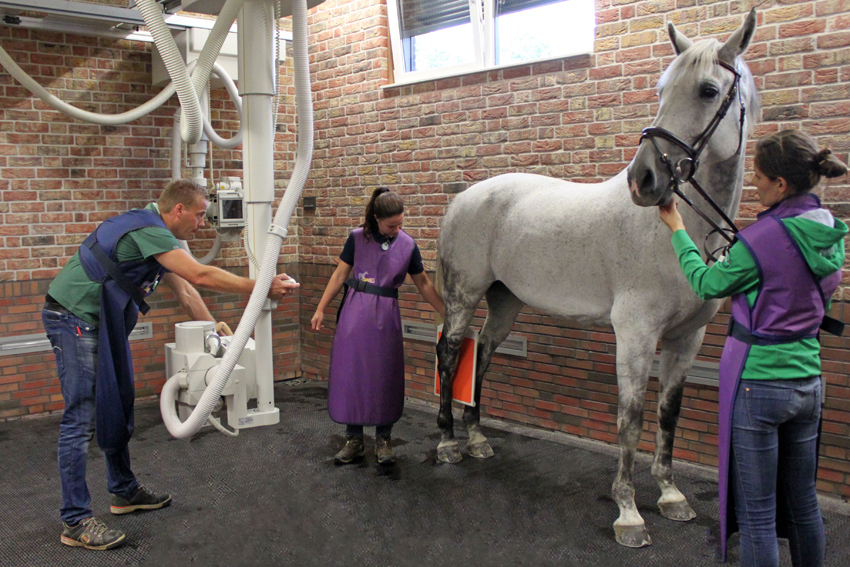
Radiographic Examination
X-rays are generated in the x-ray tube and focused on an object (for example a joint). This radiation will pass through soft tissue (tendons and muscles) and get stopped by dense tissues (bone). The remaining radiation waves finally expose the plate that is behind the object (for example a joint). On this plate and with the help of computer software this remaining radiation is converted to an image: the radiograph.
At SMDC, we have the most up to date (digital) and powerful equipment. In our radiology room we have three generators: two fixed generators that are suspended from the ceiling – one for legs and one for imaging the entire vertebral column. The third generator is a mobile one that is used for nervous horses.
Ultrasonographic Examination
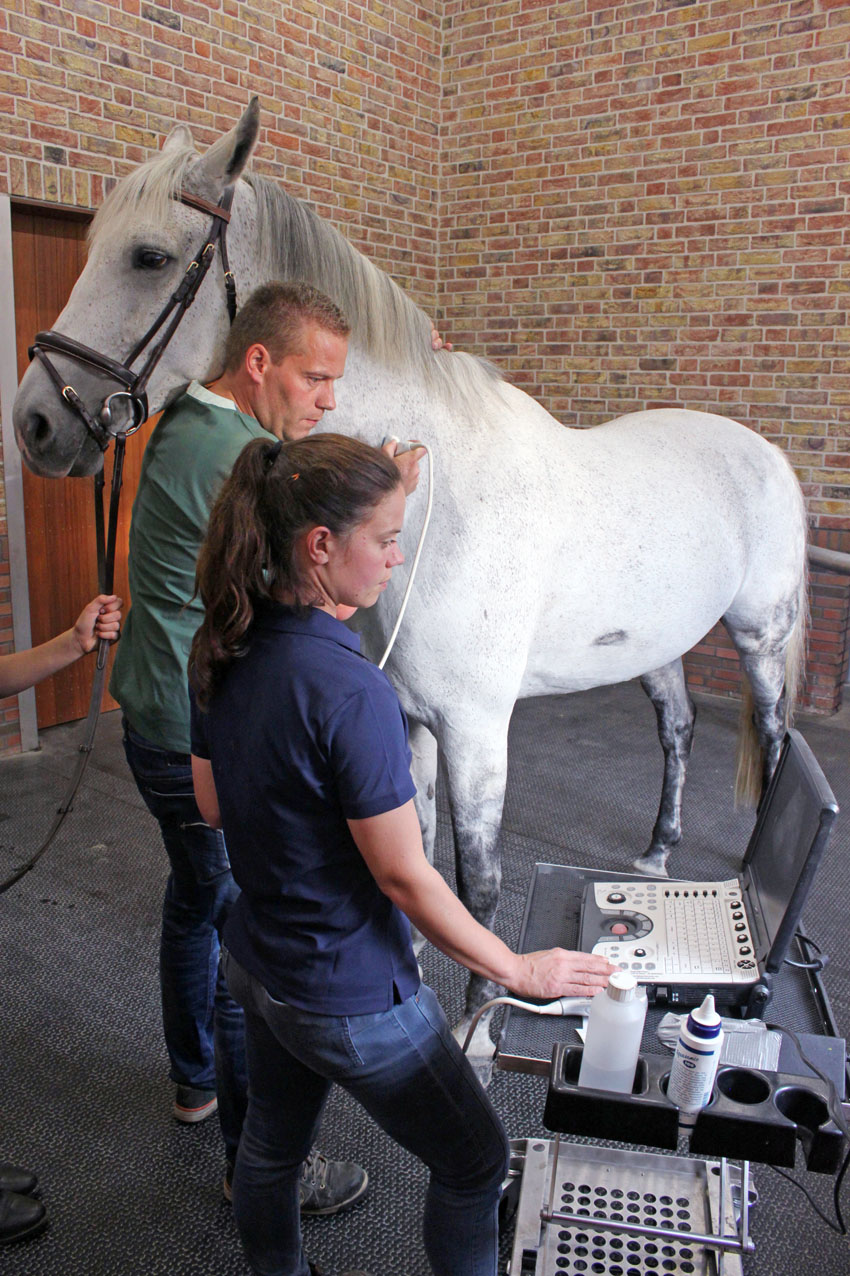
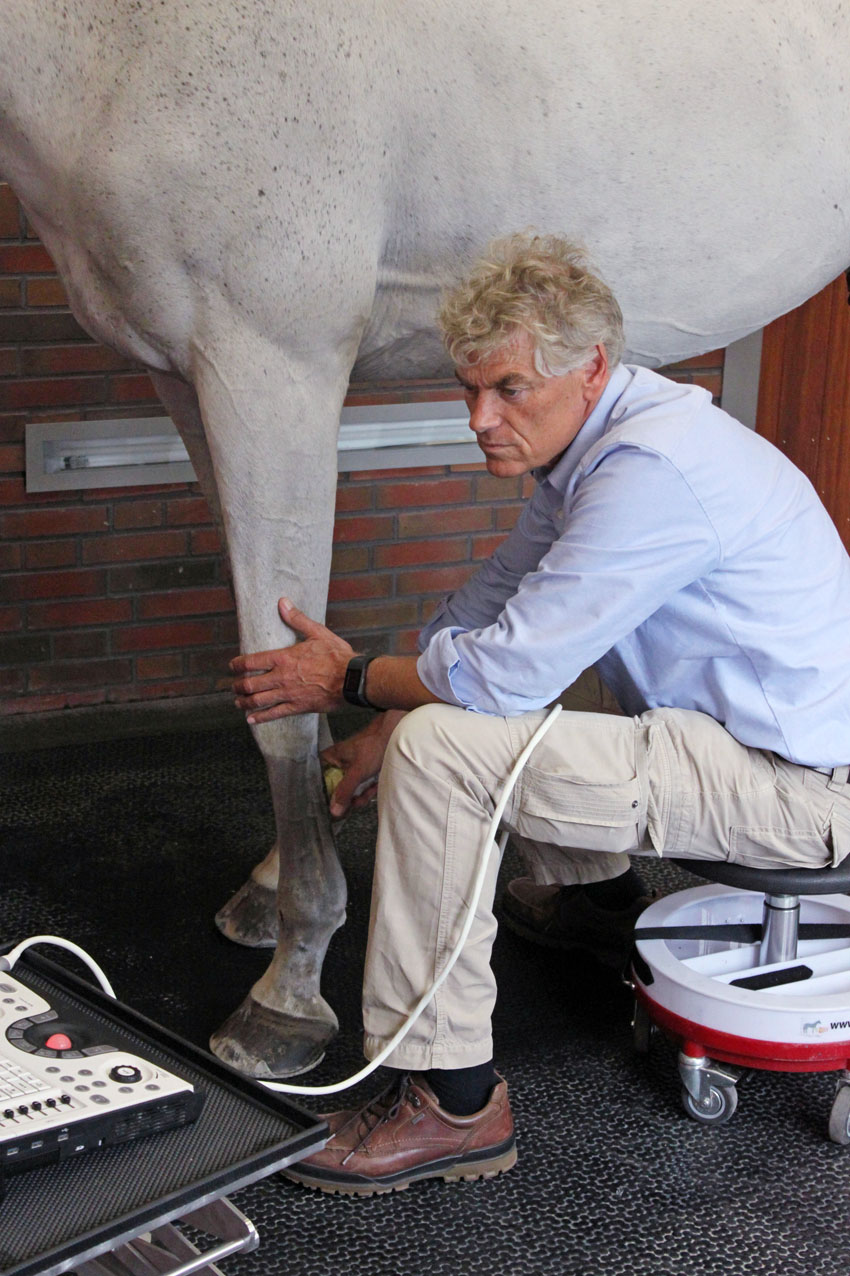
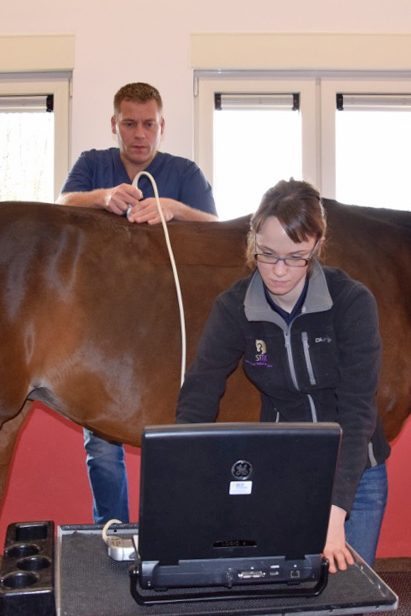
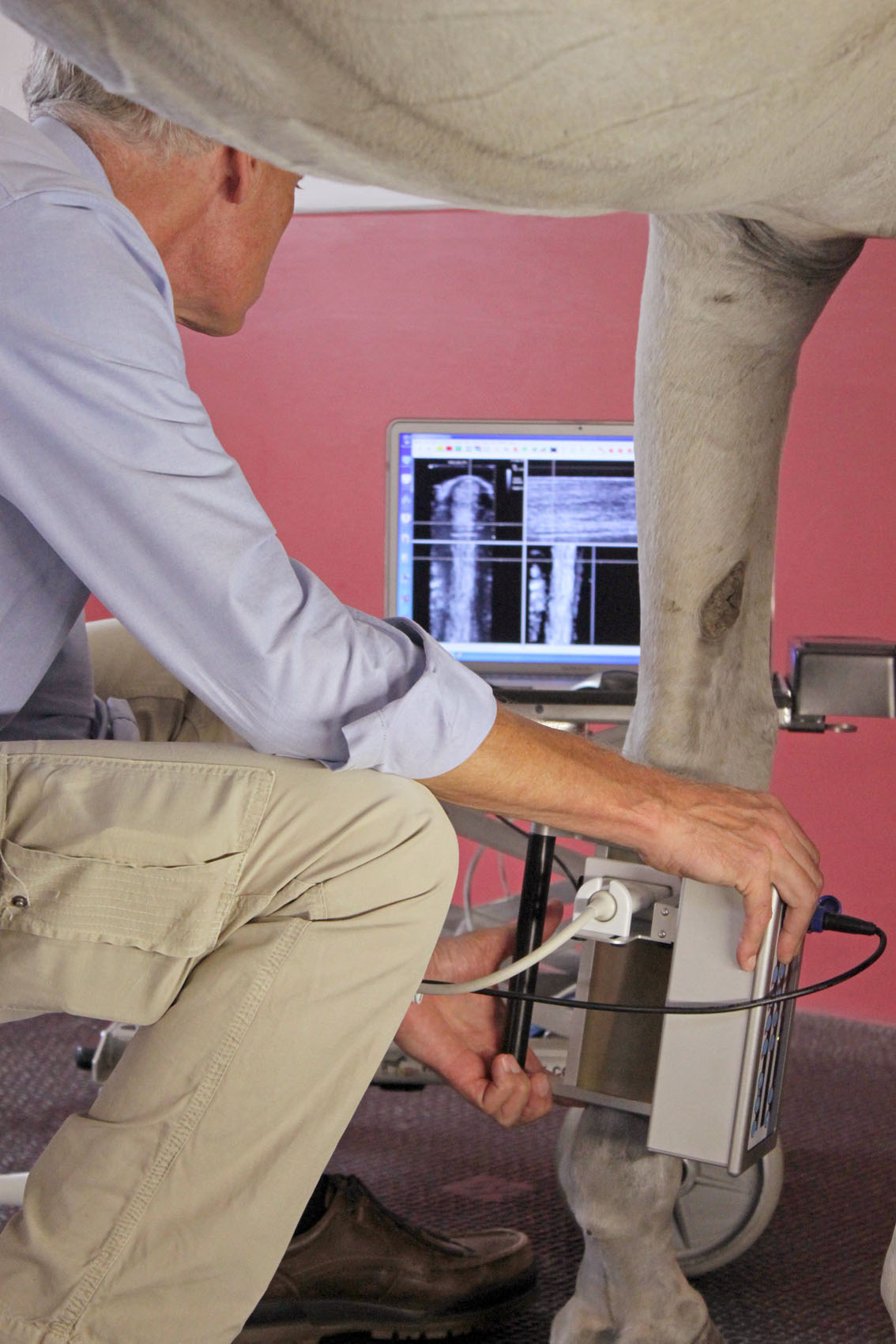
With the use of ultrasonography we can examine in detail soft tissue (skin, muscle, ligaments, tendons, cartilage and nerves) as well as the outline of bone-surfaces. We have multiple high quality ultrasounds in our clinic with multiple transducers. We use specific transducers to examine specific regions. SMDC has ISELP trained and certified specialists: this is worldwide considered the highest achievement with respect to ultrasound knowledge and experience. Ultrasonographic examinations of tendons and the axial skeleton, including trans rectal examination of the SI-joints, are performed on a daily basis at SMDC.
Tissue Characterization (UTC)
UTC Imaging is a new diagnostic scanning modality for imaging tendons and ligaments whereby the results are analyzed by a computer program. With this technique four different echo-types can be discriminated and related to the architecture and integrity of tendons and ligaments. This ultra-structural information is visualized tomographically in 3 planes of view and quantified by means of the calculation of respective percentages of echo-types. The ratios of these 4 echo-types are highly correlated with histo-morphological characteristics of tendon tissue, showing the discriminative power of UTC for tissue characterization. UTC appeared to be very sensitive which allows not only discrimination but also staging of extensive disintegration. Already minimal load induced changes in the tendon matrix, whether physiological or pathological, can be monitored with excellent inter- and intra- observer reliability.
not only discrimination but also staging of extensive disintegration. Already minimal load induced changes in the tendon matrix, whether physiological or pathological, can be monitored with excellent inter- and intra- observer reliability.
SMDC uses this technique not only on tendon and ligament lesions but also as a tool for monitoring high-performance horses aiming at injury prevention.
Scintigraphy
Equine scintigraphy (bone scan) involves injection of a radioisotope, (technetium-99m) which is linked to a compound called bisphosphonate-MDP. Within a couple of hours…
The result of the examination (made by imaging specialists) can be expected the day after the examination (so NOT the same day). The report wil be directly mailed to client and referral veterinarian(s). Together with third parties a (treatment)plan will be discussed.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. SMDC Advanced Imaging has a high quality standing MRI for horses. MRI produces highly detailed quality images that can show…
The result of the examination (made by imaging specialists) can be expected the day after the examination (so NOT the same day). The report wil be directly mailed to client and referral veterinarian(s). Together with third parties a (treatment)plan will be discussed.
Endoscopy
During laryngoscopy and bronchoscopy, a small tube with an integrated camera is passed down the airways for a thorough exam. This same principle can be applied to examine the esophagus and stomach (gastroscopy). For gastroscopy it is important that the horse is fasted with no access to food for 12 hours and no water for 6 hours.